Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Best Enlarged Prostate Treatment - Prostatomegaly - Procedure & Benefits at Curific Health Care
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
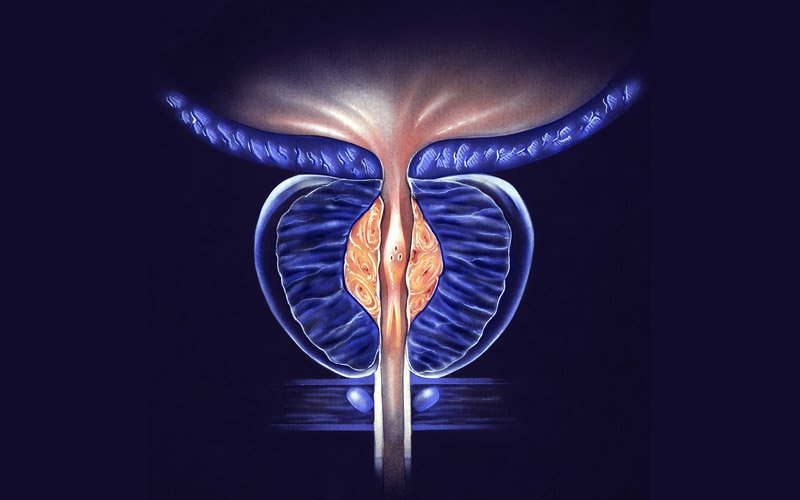
What is an Enlarged Prostate?
An enlarged prostate, medically known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. This condition is common among older men and occurs when the prostate, which surrounds the urethra, grows larger over time. As it enlarges, it may press against the urethra and bladder, leading to various urinary issues.
Symptoms of an Enlarged Prostate:
The enlargement of the prostate can cause a range of urinary symptoms, including:
- Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak urine flow or the feeling of a slow or interrupted stream
- Straining to urinate
- Urgency to urinate, even when the bladder is not full
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying after urination
These symptoms can affect a man’s daily life and overall well-being. While BPH is not life-threatening, it can lead to complications if left untreated, such as bladder infections or kidney damage.
Treatment Options:
While medication and lifestyle changes can often manage symptoms of BPH, surgery may be recommended if the condition is severe. There are several treatment options available, including:
- Medications to relax the prostate and relieve symptoms (e.g., alpha-blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors)
- Home remedies, such as reducing fluid intake before bed and avoiding caffeine or alcohol
- Surgical interventions, such as Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) or Laser Therapy, if the symptoms do not improve with medication.
Prostate Enlargement or BPH Grading
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is graded based on the severity of the symptoms, which are assessed through a combination of factors such as the AUA (American Urological Association) Symptom Index, digital rectal examination, urinalysis, and PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) measurements. This grading helps determine the best course of treatment for the condition. The grading system helps categorize BPH into four grades, each representing different levels of severity:
Grade 1 BPH: Mild Symptoms
- Symptoms: Occasional, mild urinary symptoms that cause minimal interference with daily life.
- Impact: Symptoms are generally manageable and do not significantly disrupt the patient’s quality of life.
- Management: Often, no treatment is required, but lifestyle changes may be recommended. If treatment is needed, medications may be prescribed.
Grade 2 BPH: Moderate Symptoms
- Symptoms: More frequent and bothersome urinary symptoms, such as increased urgency and weak stream.
- Impact: These symptoms begin to noticeably affect daily activities and quality of life.
- Management: Can often be managed with medications and lifestyle changes. However, if symptoms are persistent or worsen, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Grade 3 BPH: Severe Symptoms
- Symptoms: Significant obstruction in urine flow, including difficulty starting urination, frequent urination, and a weak or interrupted urine stream.
- Impact: The symptoms are severe and disruptive, significantly affecting daily activities and sleep.
- Management: Surgery is often required at this stage, although medications may be prescribed initially to help manage symptoms before surgery is considered.
Grade 4 BPH: Very Severe Symptoms
- Symptoms: Frequent urination, urgency, weak urine stream, incomplete bladder emptying, and other bothersome symptoms that disrupt daily routines and sleep.
- Impact: The symptoms significantly impact daily life and can cause complications like bladder infections or kidney damage.
- Management: Surgical intervention is typically required to relieve symptoms, restore normal urinary function, and prevent further complications.
Conclusion
BPH symptoms can range from mild to severe, and the appropriate treatment depends on the grade of the condition. If you’re experiencing urinary symptoms or suspect an enlarged prostate, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the severity and discuss possible treatment options. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Diagnostic Tests for Enlarged Prostate
When diagnosing benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or an enlarged prostate, doctors typically recommend a series of diagnostic tests to rule out other potential causes of symptoms and determine the best course of action for treatment. These tests help assess the severity of the condition and guide treatment decisions. Here’s an overview of the common diagnostic tests used:
1. Medical History Review
- Purpose: The doctor will begin by reviewing your medical history and symptoms to understand the likelihood of BPH. This includes asking about your urinary habits, any discomfort, and previous health conditions.
2. Physical Examination
- Purpose: A digital rectal examination (DRE) is performed to check the size, shape, and texture of the prostate. It helps identify abnormalities and provides an early indication of BPH or other prostate issues.
3. Urine Test
- Purpose: A urine sample is tested to rule out infections, blood in the urine, or other urinary tract issues that could cause symptoms similar to BPH. This helps narrow down the cause of the symptoms.
4. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
- Purpose: PSA levels are measured through a blood test. Elevated PSA levels may indicate an enlarged prostate, prostate infection, or even prostate cancer. While not definitive for BPH, it provides important insights.
5. Ultrasound
- Purpose: A transrectal ultrasound creates detailed images of the prostate gland. This helps determine the size of the prostate and identify any abnormalities, such as cysts or other growths.
6. Urodynamic Tests
- Purpose: These tests assess the function of the bladder and urethra. They help determine how well the bladder is emptying and the severity of urinary symptoms, which can be influenced by BPH.
7. Cystoscopy
- Purpose: A cystoscopy involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the urethra to view the bladder and prostate directly. This allows the doctor to examine any blockages or abnormalities that may be affecting urinary flow.
8. Biopsy
- Purpose: In some cases, if there’s suspicion of prostate cancer, a biopsy is performed to take a tissue sample from the prostate for further analysis.
What Prostate Enlargement Size Requires Surgery?
While there is no strict size threshold, surgery for BPH is often considered when the prostate gland is larger than 40 grams. However, the decision to proceed with surgery depends on several factors beyond prostate size, such as:
- Severity of Symptoms: Whether the symptoms are significantly affecting quality of life (e.g., frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine stream).
- Response to Medications: If medications like alpha-blockers or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are not providing adequate symptom relief.
- Other Health Conditions: The presence of complications such as bladder damage, urinary retention, or recurrent urinary tract infections.
Surgical intervention may be necessary if conservative treatments do not alleviate symptoms or if complications arise. It is important to consult with an experienced urologist to evaluate your individual condition and discuss the best treatment options, whether surgical or non-surgical.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Treatment Options for Enlarged Prostate
There are various treatment options for an enlarged prostate (BPH), and the choice of procedure depends on the severity of symptoms, prostate size, and overall health. Here are the main treatment options:
-
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): This is the most common surgical procedure for BPH. It involves using a resectoscope inserted through the urethra to remove excess prostate tissue. TURP is effective for relieving urinary symptoms in men with moderate to severe BPH. It is typically done under general or spinal anesthesia.
-
Laser Surgery: This includes techniques like photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP), holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP), and thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuLEP). Laser surgery uses laser energy to vaporize or remove excess prostate tissue. It offers the advantages of less bleeding, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery compared to traditional surgeries like TURP.
-
Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP): TUIP involves making small incisions in the prostate and bladder neck to relieve pressure on the urethra. This is suitable for men with a small to moderately enlarged prostate and less severe urinary symptoms. TUIP tends to have fewer side effects, such as retrograde ejaculation, compared to other procedures.
-
Open Prostatectomy: This is a traditional surgical method for men with very large prostates. It involves making an incision in the abdomen to remove excess prostate tissue. While effective, open prostatectomy is associated with a longer hospital stay, more blood loss, and a longer recovery time compared to minimally invasive options.
-
Robotic-Assisted Prostate Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure uses robotic instruments to perform the surgery with enhanced precision. It typically results in smaller incisions, less blood loss, and faster recovery than open surgery. Although it is most commonly used for prostate cancer, it can also be effective for BPH in certain cases.
Each of these treatments has its pros and cons, and the choice of procedure should be made after consulting with a urologist to determine the best approach based on individual needs.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Benefits of Laser Surgery for Enlarged Prostate
Laser surgery for an enlarged prostate offers several key benefits, making it an appealing treatment option for many men. These benefits include:
-
Long-lasting relief from urinary symptoms: By removing or vaporizing the obstructing prostate tissue, laser surgery can significantly improve urinary flow, reduce frequent and urgent urination, and provide long-term symptom relief. This can lead to a marked improvement in the quality of life for those suffering from BPH.
-
Minimally invasive: Laser techniques like Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) and Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP) are performed through small incisions or natural body openings. This minimizes the risk of complications, reduces recovery time, and allows patients to return to their normal activities sooner compared to traditional surgical methods.
-
Minimal risk of damage to surrounding tissue: Laser surgery provides precise and controlled removal of prostate tissue, which helps avoid damage to nearby structures, such as the urinary sphincter. This precision reduces the risk of complications like urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction that can sometimes occur with other surgical options.
-
Lower chances of urinary tract infections (UTIs): Because laser surgery typically avoids prolonged catheterization, which is often needed after traditional procedures, it lowers the risk of developing UTIs and enhances patient comfort post-surgery.
-
Long-term relief: Laser surgery has a low retreatment rate, meaning that most patients experience sustained relief from symptoms without needing additional treatments. This makes it a long-term solution for managing BPH.
Overall, laser surgery for an enlarged prostate provides several important advantages, making it an effective treatment option for many men. It offers faster recovery, fewer complications, and long-lasting symptom relief, significantly improving patients’ quality of life.
Preparation Tips Before BPH Laser Surgery
Before undergoing laser surgery for an enlarged prostate, there are a few important steps that need to be taken in order to ensure a safe and successful procedure. These preparations are crucial and should be followed closely to minimize any potential risks or complications. The following guidelines outline the necessary preparations that need to be made before undergoing laser surgery for an enlarged prostate:
- Inform your doctor about any medical conditions, allergies, or medications you are taking.
- Follow the fasting instructions provided by your doctor to ensure an empty stomach during the procedure.
- Arrange for transportation to and from the hospital, as you may not be able to drive immediately after the surgery.
- Stop taking blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or warfarin, if advised by your doctor.
- Complete any necessary pre-operative tests recommended, such as blood tests or imaging, to assess your overall health.
- Discuss any concerns or questions with your surgeon to ensure a clear understanding of the surgical procedure.
- Arrange for someone to assist you at home during the recovery period, as you may experience temporary discomfort or pain.
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing on the day of the surgery to ensure ease during the admission process.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Recovery After Laser Surgery for Enlarged Prostate
After undergoing laser surgery, it is important to follow certain guidelines and take proper care of yourself during the enlarged prostate recovery period. Here are some important pointers to keep in mind:
-
Rest and Relax: The first few days after surgery are crucial for your recovery. Make sure to get plenty of rest and avoid any strenuous activities. Take it easy and allow your body to heal.
-
Pain Management: It is normal to experience some discomfort after the surgery. Your doctor may prescribe pain medication to help manage the pain. Take the medication as instructed and inform your doctor if the pain becomes severe or persistent.
-
Fluid Intake: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated. Water is the best choice, but you can also have clear soups, herbal teas, and diluted fruit juices.
-
Urination and Bladder Control: After the catheter is removed, you may experience some difficulty with urination and bladder control. This is normal and should improve over time. It is important to practice and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles to regain control.
-
Diet and Nutrition: Follow a healthy and balanced diet to support your recovery. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid spicy and acidic foods that may irritate your urinary tract.
-
Physical Activity: Gradually increase your physical activity as you start feeling better. Start with light exercises, such as walking, and gradually progress to more strenuous activities. However, avoid heavy lifting or any activities that put strain on your pelvic area.
-
Follow-up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your doctor. These appointments are important for monitoring your progress and addressing any concerns or complications that may arise.
-
Sexual Activity: It is common to experience changes in sexual function after enlarged prostate laser surgery. Talk to your doctor about any concerns or questions you may have. They can provide guidance and recommend appropriate treatments or therapies if necessary.
Each person’s recovery may vary, and it is important to follow your doctor’s specific instructions for a successful recovery after enlarged prostate laser surgery. If you have any questions or concerns during your recovery period, do not hesitate to contact your doctor.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Risk Factors For Enlarged Prostate
The below mentioned are some risk factors that may increase the risk of the prostate gland enlargement in men.
- Age: The risk of developing an enlarged prostate increases with age. It is more common in men over the age of 50.
- Family history: Having a family history of enlarged prostate or prostate cancer can increase the risk.
- Hormonal imbalances: Changes in hormone levels, specifically a decrease in testosterone and an increase in estrogen, can contribute to the development of an enlarged prostate.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese has been linked to an increased risk of enlarged prostate.
- Ethnicity: Studies have shown that certain ethnic groups, such as African-American and Caribbean men, are more prone to developing an enlarged prostate.
- Lifestyle factors: Certain lifestyle choices, such as a sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity, and poor diet, may increase the risk.
- Smoking: Smoking has been associated with an increased risk of enlarged prostate.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, have been linked to an increased risk of enlarged prostate.
- Medications: Some medications, such as certain alpha-blockers used to treat high blood pressure, can increase the risk of developing an enlarged prostate.
- Other factors: Other factors that may contribute to the risk of an enlarged prostate include chronic inflammation, urinary tract infections, and exposure to certain chemicals or toxins.
These risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing an enlarged prostate, but it is important to note that not all men with these risk factors will develop BPH. Regular check-ups and discussions with a doctor can help identify any potential issues and determine the best course of action for prevention or treatment.
Lifestyle Changes For Enlarged Prostate
While medical treatments are available, making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage the symptoms of an enlarged prostate. Here are some pointers to consider:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put extra pressure on the bladder and worsen urinary symptoms. Therefore, it is important to maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals. Avoiding high-calorie, sugary foods and beverages can also help in managing your weight.
- Stay Active: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve overall health and help manage symptoms of an enlarged prostate. Activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling can all be beneficial. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, as recommended by healthcare professionals.
- Limit Fluid Intake: Drinking excessive amounts of fluids, especially before bedtime, can lead to more frequent urination during the night. To reduce nighttime trips to the bathroom, it is advisable to limit fluid intake, especially alcohol and caffeine, in the evening. However, make sure to stay adequately hydrated throughout the day.
- Practice Bladder Control Techniques: Delaying urination when you feel the urge to go can help strengthen the bladder muscles and improve control over urinary symptoms. It is also recommended to double void, which involves urinating, waiting a few seconds, and then urinating again. This helps ensure the bladder is emptied more fully.
- Prevent Constipation: Straining during bowel movements can put pressure on the prostate gland and worsen urinary symptoms. To prevent constipation, include fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Drinking plenty of water and staying physically active can also help regulate bowel movements.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate urinary symptoms and impact overall well-being. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, exercising regularly, and engaging in hobbies, can be beneficial. Consider incorporating activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine.
- Follow a Healthy Diet: Consuming a well-balanced diet that is low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can be beneficial for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms. Some studies suggest that certain foods, such as tomatoes, broccoli, green tea, and fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, may have a positive effect on prostate health.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Enlarged Prostate
Here are some non-surgical techniques to get relief from the symptoms of an enlarged prostate gland.
-
Medications: One of the non-surgical treatments for an enlarged prostate is the use of medications. There are different types of drugs that can help manage the symptoms of an enlarged prostate, such as alpha blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. Alpha blockers relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder, making it easier to urinate. On the other hand, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors work by shrinking the prostate gland over time. These medications can be prescribed by a healthcare professional and should be taken as directed.
-
Urethral Stents: Urethral stents are small mesh tubes that are inserted into the urethra to help keep it open and allow for improved urine flow. This can be an option for individuals who are not suitable candidates for surgery or other non-surgical treatments. Urethral stents can be placed in a minimally invasive procedure and are designed to provide relief from urinary symptoms caused by an enlarged prostate. However, it is important to note that stents may have limitations and potential complications, which should be discussed with an experienced urologist.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: In addition to medical treatments, making certain lifestyle modifications can also help manage the symptoms of an enlarged prostate. These modifications may include avoiding caffeine and alcohol, limiting fluid intake before bedtime, and practicing pelvic floor exercises. Maintaining a healthy weight and staying physically active can also be beneficial. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate lifestyle changes for individual circumstances.
Home Remedies for Prostate Gland Enlargement Treatment
Here are a few home remedies that may help alleviate the symptoms of prostate enlargement:
-
Saw Palmetto: This herb has been traditionally used to treat urinary symptoms associated with prostate enlargement. Saw palmetto extract is believed to reduce inflammation and help shrink the prostate gland, thereby improving urinary flow and reducing frequent urination.
-
Pygeum: Derived from the bark of the African cherry tree, pygeum has been used for centuries to treat urinary problems. It is believed to reduce inflammation in the prostate and improve urinary function.
-
Stinging Nettle: Stinging nettle root extract has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help relieve urinary symptoms associated with prostate enlargement. It is believed to inhibit the production of certain hormones that contribute to prostate growth.
-
Beta-Sitosterol: This natural plant extract is commonly found in fruits, vegetables, and nuts. It has been shown to improve urinary symptoms, reduce inflammation, and help shrink the prostate gland.
-
Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants, green tea has been associated with various health benefits, including the potential to reduce the risk of prostate enlargement. The polyphenols found in green tea are believed to have anti-inflammatory properties that could help alleviate symptoms.
-
Pumpkin Seeds: These seeds are a good source of zinc, which is important for prostate health. Consuming pumpkin seeds regularly may help reduce symptoms associated with prostate enlargement, such as frequent urination and weak urine flow.
There are several home remedies that may help manage the symptoms of prostate enlargement. However, it is crucial to prioritize medical guidance and consult with an experienced urologist before attempting any self-treatment.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
What Happens If Enlarged Prostate Is Left Untreated?
If an enlarged prostate is left untreated, it can lead to several serious complications:
-
Urinary Problems: As the prostate grows in size, it can press against the urethra, leading to difficulty in urination. Symptoms can include frequent urination, weak urine flow, difficulty starting urination, incomplete bladder emptying, and urinary retention.
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): The obstruction of urine flow caused by an untreated enlarged prostate can result in stagnant urine, creating a breeding ground for bacteria. This increases the risk of urinary tract infections, which may lead to pain or burning during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, lower abdominal pain, and increased urinary frequency.
-
Bladder Stones: Chronic urinary retention can lead to the formation of bladder stones. These stones develop from concentrated urine that doesn’t fully empty from the bladder. Symptoms of bladder stones include abdominal pain, blood in urine, frequent urination, and difficulty urinating.
-
Kidney Damage: If urine accumulates in the bladder due to an untreated enlarged prostate, it can increase pressure on the kidneys, potentially causing damage. Over time, this can lead to kidney stones, infections, and even kidney failure.
-
Acute Urinary Retention: In severe cases, an untreated enlarged prostate can cause acute urinary retention, where the bladder is completely unable to empty. This condition is extremely painful and requires immediate medical attention.
-
Increased Risk of Prostate Cancer: While an enlarged prostate itself doesn’t directly cause prostate cancer, the chronic inflammation and urinary retention associated with BPH may potentially increase the risk of cancerous growth in the prostate.
In conclusion, leaving an enlarged prostate untreated can result in a range of serious complications, so seeking medical advice and treatment is crucial if symptoms arise.
Enlarged Prostate vs. Prostate Cancer
Both an enlarged prostate and prostate cancer affect the prostate gland, but they are distinct conditions with different causes and implications:
-
Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia – BPH):
- Cause: A non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate, commonly occurring as men age.
- Symptoms: Frequent urination, weak urine flow, difficulty emptying the bladder.
- Treatment: Can usually be managed with medications or surgery and is not life-threatening.
-
Prostate Cancer:
- Cause: The abnormal growth of prostate cells that may spread to other parts of the body.
- Symptoms: Urinary problems, blood in urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, pain in the back, hips, or pelvis.
- Treatment: Requires prompt medical intervention, often involving surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
Although both conditions share urinary symptoms, BPH is a benign condition, while prostate cancer can be life-threatening. Regular screenings and early detection are important for managing prostate cancer.