Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Epididymal Cyst - Treatment Procedure & Benefits at Curific Health Care
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
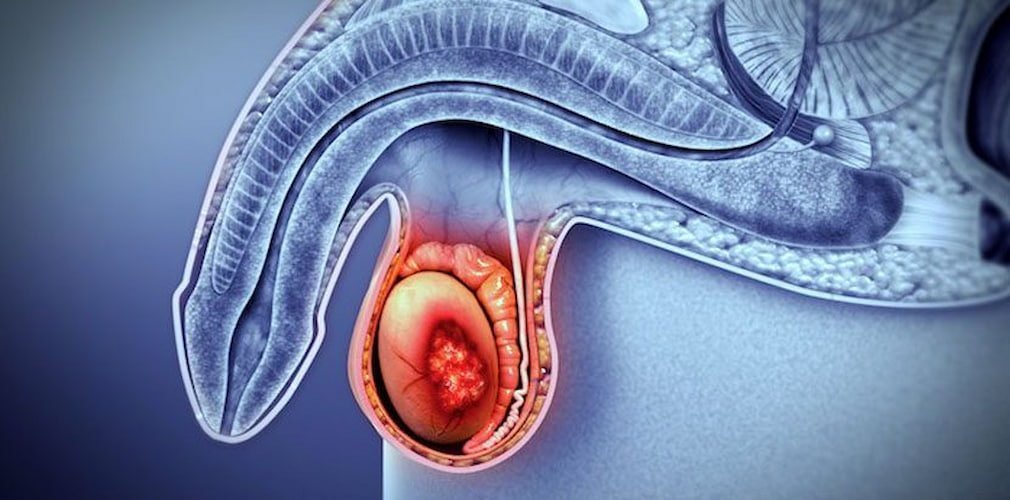
What Is Epididymal Cyst ?
Epididymal cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in the epididymis, a coiled tube at the back of the testicle. These cysts are generally benign and often asymptomatic. Treatment is only required when the cysts cause discomfort, become symptomatic, or impact fertility.
Common Treatment Options:
Observation
- If the cyst is small and asymptomatic, no treatment is needed. Regular monitoring may be recommended.
Aspiration
- A needle is used to drain the fluid from the cyst. While this provides temporary relief, cysts may refill over time, making recurrence likely.
Percutaneous Sclerotherapy
- After aspiration, a sclerosing agent is injected into the cyst to prevent fluid accumulation and recurrence.
Surgery
- Epididymal Cystectomy: Surgery is the most effective treatment for symptomatic cysts. During the procedure, the cyst is completely removed to prevent recurrence.
- It is typically recommended for larger cysts causing discomfort or fertility issues.
Recovery and Risks of Surgery
- Recovery from surgery is usually quick, with minimal downtime.
- Potential risks include infection, bleeding, or damage to the epididymis, which could affect fertility.
When to Seek Treatment
If the cyst causes pain, swelling, or interferes with daily activities or fertility, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
By addressing the issue promptly, patients can avoid complications and improve their quality of life.
PCNL Surgery is highly effective for stones larger than 2 cm and has largely replaced traditional open surgeries due to its minimally invasive nature, reduced pain, and quicker recovery. It is designed to relieve painful symptoms caused by large kidney stones with minimal complications, enabling patients to resume their normal lives with ease.
For expert care and affordable PCNL surgery costs, consult Curific Health Care today.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
How Does an Epididymal Cyst Form?
The epididymis, a coiled tube located at the back of the testicle, is responsible for storing and transporting sperm. An epididymal cyst forms when fluid, sperm, or both fail to drain properly into the vas deferens, resulting in a buildup within the epididymis. This can lead to the formation of a fluid-filled sac, known as a cyst, or a spermatocele if it contains sperm.
Causes of Epididymal Cysts:
- Blockage in sperm flow: Obstructions in the epididymal ducts can trap sperm and fluid, causing accumulation.
- Injury or trauma: Any damage to the testicle or epididymis may trigger cyst formation.
- Infections or inflammation: Epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis) can sometimes result in cyst development.
- Congenital abnormalities: Some epididymal cysts may develop during embryonic growth and remain undetected until adulthood.
Symptoms:
- Epididymal cysts are usually painless and may go unnoticed for years.
- When symptoms appear, they include:
- A lump or swelling in the scrotum.
- Discomfort or heaviness in the testicle.
- Rarely, pain or tenderness.
Though typically harmless, large or symptomatic cysts may require treatment, especially if they interfere with daily activities or fertility. If symptoms worsen, consulting a healthcare provider is essential.
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Symptoms of Epididymal Cyst
In most cases, epididymal cysts remain asymptomatic, causing no discomfort or noticeable changes. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Presence of a lump: A soft, painless lump may develop at the top or bottom of one or both testicles.
- Heaviness in the scrotum: A sensation of heaviness or fullness may be felt.
- Redness and swelling: The scrotum may appear red or swollen due to the cyst.
- Groin pain: Some individuals may experience mild to moderate pain in the groin area.
If any of these symptoms appear, it is important to consult a medical professional promptly to determine the cause and the need for treatment.
How is an Epididymal Cyst Diagnosed?
Epididymal cysts are often detected incidentally during self-exams or routine physical examinations. The diagnostic process includes:
Physical Examination:
- A healthcare provider palpates the testicles and epididymis to identify lumps or abnormalities.
- A light may be shone through the scrotum (transillumination) to determine if the lump is fluid-filled (indicative of a cyst) or solid (requiring further evaluation).
Ultrasound:
- Ultrasound imaging is a common diagnostic tool for confirming the presence of an epididymal cyst.
- This test provides detailed images of the testicles and surrounding structures to evaluate the cyst’s size, location, and composition.
Additional Tests (if necessary):
- In cases where the lump appears suspicious or atypical, further tests may be performed to rule out other conditions like:
- Infection (indicated by tenderness, redness, or warmth).
- Testicular cancer (requires biopsy).
- Hernia (often associated with swelling).
- In cases where the lump appears suspicious or atypical, further tests may be performed to rule out other conditions like:
Early diagnosis through these methods helps differentiate epididymal cysts from other, potentially serious conditions and ensures appropriate management.
What Happens During an Epididymal Cystectomy or Excision?
Epididymal cystectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove a cyst from the epididymis. Here’s a step-by-step overview of the process:
Anesthesia Administration:
- The procedure begins in the operating theater.
- General anesthesia is commonly used to ensure you are unconscious during the surgery.
- If general anesthesia is unsuitable, spinal anesthesia may be used to numb the lower half of your body.
Incision:
- A small incision is made in the scrotum to access the epididymis and the cyst.
Cyst Removal:
- The surgeon carefully maintains the blood supply to the epididymis while draining or removing the cyst.
- Surrounding tissues are handled delicately to avoid any damage.
Closure:
- After the cyst is successfully removed, the incision is closed using dissolvable stitches.
Post-Surgery Monitoring:
- After the procedure, you will be moved to the observation room where medical staff monitor your vital signs as you wake up from anesthesia.
- Once stable, you’ll be transferred to the recovery room for further monitoring.
This minimally invasive surgery is typically safe and effective, with most patients recovering fully within a few weeks. Following the surgery, your doctor will provide aftercare instructions to ensure proper healing.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Different Techniques for Epididymal Cyst Treatment
Epididymal cyst treatment varies based on the cyst’s size, symptoms, and impact on the patient. For asymptomatic cysts, observation and monitoring are often sufficient. When treatment becomes necessary, the following techniques may be used:
Aspiration:
- A minimally invasive procedure where a needle is used to drain the fluid from the cyst.
- Provides temporary relief but may not be permanent, as the cyst can refill with fluid over time.
Percutaneous Sclerotherapy:
- A sclerosing agent, such as ethanol, is injected into the cyst to harden and shrink it, preventing fluid accumulation.
- After about 20 minutes, the sclerosing agent is aspirated, and the patient is monitored for a few weeks for recurrence.
Microsurgical Epididymal Cystectomy:
- A less invasive procedure performed using an operating microscope to remove the cyst while preserving surrounding tissues.
- Typically recommended for moderate-sized cysts.
Epididymal Cyst Excision:
- A more invasive procedure involving the removal of part of the epididymis along with the cyst.
- Suitable for larger or complex cysts that cannot be managed with cystectomy alone.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as cyst size, location, symptoms, and overall health. Patients should discuss options with their doctor to understand the risks, benefits, and recovery process.
What to Expect After Testicular Cyst Removal
Following epididymal cyst removal surgery, the recovery process typically involves the following:
Scrotal Support:
- A supportive garment is provided to restrict movement and prevent strain on stitches.
Pain Management:
- Mild pain and discomfort around the scrotum can occur, which is managed with prescribed medications.
Restricted Mobility:
- Walking and other movements may be challenging for the first few days. Adequate rest is essential for proper healing.
Monitoring Post-Surgery:
- Medical staff will observe the patient’s vitals, including blood pressure and heart rate, for a few hours after surgery.
Discharge and Recovery Plan:
- Once the patient can urinate and is stable, they are discharged with detailed recovery instructions and a follow-up schedule.
Proper care and adherence to the doctor’s advice can ensure a smooth recovery and reduce the risk of complications. If you experience severe pain, swelling, or signs of infection, seek immediate medical attention.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Epididymal Cyst Treatment Cost in India
The cost of epididymal cyst surgery in India typically ranges between ₹25,000 and ₹70,000. The final cost depends on multiple factors, such as:
- Size and Location of the Cyst: Larger or more complicated cysts may require advanced procedures, increasing the cost.
- Surgeon’s Expertise: Highly experienced surgeons may charge higher fees.
- Type of Procedure: Techniques like minimally invasive surgery or microsurgical cystectomy tend to cost more than conventional methods.
- City of Treatment: Metros and larger cities usually have higher treatment costs than smaller cities.
- Hospital Type: The choice between a private or government hospital and the facilities provided significantly impacts costs.
- Hospitalization and Post-Surgical Care: Expenses related to hospital stays, medications, and aftercare services also affect the total price.
For a precise estimate, consult with healthcare providers or specific hospitals offering the procedure.
Recovery After Epididymal Cyst Removal
Recovery from epididymal cyst removal typically takes around 2-3 weeks. The recovery process depends on factors like the surgical technique used and the patient’s overall health. Below are some tips to ensure smooth recovery:
Supportive Care:
- Wear scrotal support or snug underpants to stabilize the treated area and minimize discomfort.
Medication:
- Follow your doctor’s prescription for pain relievers, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory medications to control pain, swelling, and prevent infection.
Cold Compress:
- Use ice packs on the scrotum multiple times a day for the first few days to reduce swelling and bruising.
Avoid Strenuous Activities:
- Refrain from heavy lifting, sexual activity, or vigorous physical activities until cleared by your doctor.
Wound Care:
- Keep the surgical incision clean and dry. Change dressings as instructed by your doctor to reduce the risk of infection.
Follow-Ups:
- Regular check-ups with the surgeon are crucial to monitor healing and address any complications promptly.
Most patients can resume daily activities within a couple of weeks, but complete recovery may take a little longer depending on individual circumstances.