Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Meniscus Tear Treatment- Surgery Procedure & Benefits at Curific Health Care
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
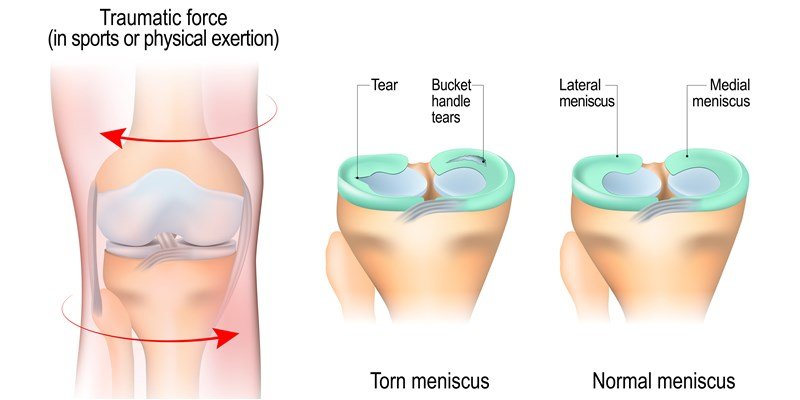
What is a Meniscus Tear?
A meniscus tear is a common injury to the knee joint involving the meniscus, a C-shaped cartilage structure that acts as a shock absorber and provides stability to the knee. Tears typically occur due to forceful twisting or rotating motions, often during sports or heavy lifting. Over time, degenerative changes can weaken the meniscus, increasing the risk of tears, particularly in older adults.
Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear:
- Knee pain and swelling
- Stiffness and difficulty straightening the knee
- Locking or catching sensations in the knee
- Popping or clicking sounds during movement
- Limited range of motion
Diagnosis:
An orthopedic surgeon evaluates meniscus tears through a physical examination and imaging tests such as an MRI, which helps determine the location, size, and severity of the tear.
Treatment Options:
- Conservative Treatment: Suitable for minor tears, involving rest, ice, physical therapy, and supportive devices such as crutches or knee braces.
- Surgical Intervention: Required for severe tears, with procedures to either repair or remove the damaged portion of the meniscus.
Grading of Meniscus Tears:
- Grade 1: Minor fraying, often managed conservatively.
- Grade 2: Moderate damage, requiring a mix of conservative and surgical options depending on symptoms and activity level.
- Grade 3: Complete tear, usually needing surgical repair or removal for optimal recovery.
Prompt medical attention is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of long-term knee complications.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Meniscus Tear Diagnosis
An orthopedic surgeon begins the diagnosis of a meniscus tear with a thorough physical examination. This includes evaluating the symptoms, the intensity of knee pain, any past injuries, and checking for tenderness and swelling around the affected area. The doctor may also perform specific knee movement tests to assess the severity of the tear.
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the injury, the following diagnostic tests are typically recommended:
- MRI: Provides a detailed image of the meniscus, surrounding tissues, and ligaments, helping to identify the location and severity of the tear.
- X-Ray: Helps detect any underlying bone problems in the knee joint that may contribute to the symptoms.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential to decide the appropriate treatment plan and ensure proper recovery.
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Meniscus Tear Treatment Options
The treatment options for a meniscus tear depend on the severity and location of the tear, as well as the patient’s overall health and activity level. The main options include:
Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for a torn meniscus is knee arthroscopy, a minimally invasive surgery typically performed under anesthesia. The procedure usually lasts less than an hour and involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The surgeon cleans the knee area and covers the leg with a sterile drape. A clamp is placed on the upper thigh to help position the knee during the procedure.
- Portals and Visualization: Small incisions, called portals, are made in the knee. The joint is filled with sterile fluid to control bleeding and clear debris, improving visibility for the surgeon.
- Arthroscope Insertion: A thin tube with a light and camera (arthroscope) is inserted through one of the portals. It transmits images to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to examine the tear.
Based on the location and severity of the tear, the surgeon may proceed with one of the following:
Meniscus Repair:
- Suitable for tears in the outer region of the meniscus, where blood supply promotes healing.
- The torn pieces of cartilage are stitched together to allow natural healing.
- Repairable tears are less common, accounting for less than 10% of cases.
Partial Meniscectomy:
- Performed for tears in the inner region of the meniscus, where blood supply and healing potential are limited.
- Damaged cartilage is trimmed and removed, leaving healthy tissue intact.
- Closure: Once the repair or removal is complete, the portals are closed with stitches or surgical strips, and the knee is covered with a bandage.
Both procedures are designed to alleviate pain, restore knee function, and prevent further damage to the joint.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Meniscus Tear
Non-surgical treatment options for a meniscus tear aim to relieve symptoms, promote healing, and improve knee function without surgery. These methods are typically recommended for minor tears, stable injuries, or individuals who cannot undergo surgery. The key non-surgical treatments include:
Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter analgesics like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, are used to reduce pain and swelling.
- Topical NSAIDs: Creams or gels containing NSAIDs can provide localized pain relief.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In more severe cases, injections may be used to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. These provide temporary relief but do not repair the tear itself.
- Note: Medications address symptoms but cannot heal the meniscus tear. For severe tears, surgery may still be required.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is crucial for improving knee strength, flexibility, and stability while reducing pain. A personalized program designed by a physical therapist may include:
- Strengthening Exercises: To target muscles around the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, for better joint support.
- Flexibility Exercises: Gentle stretches to maintain or improve knee flexibility and prevent stiffness.
- Balance and Proprioception Training: To enhance stability and prevent future injuries.
- Pain Management Techniques: Ice, heat, or electrical stimulation may be used during therapy sessions.
Injections
Injections are often used in conjunction with other conservative treatments to manage symptoms:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
- Viscosupplementation: Injections of hyaluronic acid to improve joint lubrication and reduce friction within the knee.
- Limitations: While injections help manage symptoms, they do not heal the tear and are typically part of a broader treatment plan.
These conservative methods can be highly effective for minor tears or as an initial approach before considering surgical options. A healthcare professional will recommend the best course of action based on the tear’s location, severity, and individual patient factors.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Preparation Before Meniscus Tear Surgery
Proper preparation for meniscus tear surgery ensures a smoother procedure and recovery. Here are essential steps to follow:
- Consultation with the Doctor: Share detailed information about your knee injury, medical history, and any medications or supplements you are taking. This helps the doctor plan the surgery effectively.
- Diagnostic Tests: Complete all recommended diagnostic tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, to confirm the severity and type of tear.
- Dietary Changes: Avoid eating or drinking anything for at least 8 hours before surgery to reduce the risk of anesthesia-related complications.
- Home Preparation: Arrange your home for post-surgical recovery. Make it accessible and comfortable by setting up a recovery space, removing tripping hazards, and placing essential items within easy reach.
Benefits of Meniscus Tear Treatment
Meniscectomy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, offers several advantages over traditional methods of meniscus repair:
- Faster Recovery: Patients experience quicker healing with less discomfort.
- Minimal Bleeding: The advanced technique reduces the risk of excessive bleeding during the procedure.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Fewer post-surgical complications, such as infection or swelling, are associated with this method.
- Smaller Incisions: The procedure involves smaller incisions, leading to reduced scarring.
- Higher Success Rate: Minimally invasive surgery often has better outcomes compared to conventional techniques.
These benefits make minimally invasive meniscus tear treatments a preferred choice for faster and safer recovery.
Recovery After Meniscus Tear Surgery
The recovery process following meniscus tear surgery largely depends on the severity of the tear and the surgical technique used. Complete recovery typically takes about 4-6 months, though limited physical activities, such as walking, can often resume within a week. Here are key recovery tips:
- Pain Management: Avoid activities that strain the knee or cause excessive pain. Use prescribed medications as directed to manage discomfort effectively.
- Physical Therapy: Adhere to the physiotherapy plan provided by your doctor or therapist. Perform exercises consistently but avoid overexertion, as it can hinder the healing process.
- Rest: Take sufficient rest and avoid rushing back to daily activities. Rest promotes healing and reduces the risk of complications.
Risks & Complications Associated with Meniscus Tear Surgery
Like any surgery, meniscus tear surgery involves potential risks and complications. While these are generally rare, it’s important to be aware of them:
- Infection: There is a minor risk of infection at the surgical site, which can be minimized through sterilization and antibiotics.
- Bleeding and Blood Clots: Surgery may cause bleeding, and in rare cases, blood clots may form, leading to complications.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: A slight risk exists for accidental injury to surrounding nerves or blood vessels, potentially causing numbness or tingling.
- Knee Stiffness: Some patients may experience stiffness, limiting joint mobility and requiring additional rehabilitation.
- Persistent or Recurrent Symptoms: In rare cases, the meniscus may not heal completely, or symptoms may return, necessitating further treatment.
- Anesthetic Complications: Anesthesia carries minimal risks, such as adverse reactions or respiratory issues, though these are uncommon.
- Rehabilitation Challenges: Recovery may involve rigorous physical therapy, and non-compliance can hinder successful outcomes.
Positive Outlook
The risks associated with meniscus tear surgery are generally low, and most individuals achieve favorable results with proper post-surgical care and rehabilitation. Following medical advice and staying committed to recovery protocols can significantly improve outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes After Meniscus Tear Surgery
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can significantly aid recovery and reduce the risk of re-injury following meniscus tear surgery:
- Rest and Recovery: Allow ample time for healing and adhere to activity restrictions recommended by your doctor. Gradually reintroduce activities as per medical advice.
- Physical Therapy: Commit to a structured rehabilitation program to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Attend all therapy sessions and follow the prescribed exercises.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Manage your weight to reduce pressure on your knee joint. Opt for a balanced diet and engage in approved physical activities to maintain overall health.
- Protect Your Joints: Avoid high-impact sports or activities that involve twisting or pivoting. Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to stay active without straining the knee.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Use supportive shoes with good cushioning to minimize stress on the knee during daily movements.
- Strengthening Exercises: Continue strengthening the muscles around the knee even after completing formal physical therapy. This helps maintain stability and prevents future injuries.
- Regular Follow-ups: Keep up with scheduled appointments to monitor your progress and get personalized advice on returning to daily and athletic activities.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Meniscus Tears
For mild to moderate meniscus tears, non-surgical approaches can help manage symptoms and support healing:
- Rest: Avoid putting weight on the injured knee. Use crutches or wear a brace to reduce strain.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs to the knee for 20–30 minutes every 3–4 hours for several days to reduce swelling.
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage or knee sleeve to control swelling and provide support.
- Elevation: Elevate the leg with a pillow under the heel to minimize swelling.
- Medications: Use pain relievers or NSAIDs like ibuprofen as prescribed by a doctor to reduce inflammation and discomfort.
- Exercises: Perform doctor-recommended stretching and strengthening exercises to relieve joint stress and improve mobility. Avoid overexerting the knee during these exercises.
- Avoid High-Impact Activities: Refrain from running, jumping, or any activity that may worsen the injury until the knee is fully healed.
Key Considerations
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment plan or exercise routine. Recovery strategies should be tailored to your specific condition for the best outcomes.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Signs of a Healing Meniscus Tear
Here are some common signs that indicate progress in healing a meniscus tear:
- Pain Reduction: A noticeable decrease in knee pain is often the first sign of healing. Activities that once caused discomfort may become less painful.
- Improved Range of Motion: As the knee heals, you may regain flexibility and find it easier to perform movements that were previously restricted.
- Reduced Swelling: Swelling in the knee diminishes gradually as healing progresses. While some mild swelling may persist for a time, significant improvement is a positive sign.
- Resumption of Activities: Under medical supervision, you may begin returning to regular activities, including light exercises or sports. Progressing gradually through a rehabilitation program is key to avoiding re-injury.
Important Notes
Healing timelines vary based on the severity of the tear and individual factors like age, activity level, and adherence to treatment plans. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations, including physical therapy, and allow adequate time for recovery to ensure optimal healing.