Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Testicular Torsion Surgery - Twisted Testicle - Treatment Procedure & Benefits at Curific Health Care
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
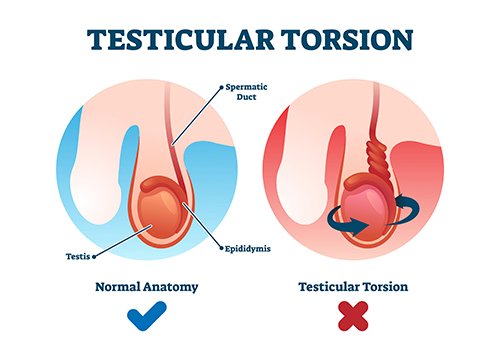
What is Testicular Torsion (Twisted Testicle)?
Testicular torsion, also known as twisted testicle or scrotal torsion, is a rare but serious medical condition where the spermatic cord, which supplies blood to the testicle, twists and blocks blood flow. This condition can occur at any age but is most common in adolescent boys aged 12 to 18. It is considered a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
The condition is characterized by sudden and severe pain in the affected testicle, often accompanied by swelling, redness, and tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal discomfort.
There are two main types of testicular torsion:
- Intravaginal Torsion: The spermatic cord twists within the tunica vaginalis, the membrane surrounding the testicle.
- Extravaginal Torsion: The twist occurs outside the tunica vaginalis, usually within the inguinal canal.
If not treated promptly, testicular torsion can lead to testicular infarction, where the lack of blood supply causes the tissue to die. This can result in the loss of the testicle and complications such as infertility.
Treatment
Surgery is the primary treatment for testicular torsion. During the procedure, the surgeon untwists the spermatic cord and secures the testicle to prevent further torsion. If the testicle is severely damaged due to a prolonged lack of blood flow, it may need to be surgically removed.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Testicular Torsion Symptoms
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that demands immediate attention to prevent permanent damage or loss of the affected testicle. Symptoms can vary depending on the severity and duration of the condition. Below are the most common symptoms:
Severe Pain in One Testicle
Sudden, intense pain is the most prominent symptom. The discomfort may develop abruptly or gradually and is often accompanied by nausea or vomiting.Swelling and Redness
The affected testicle typically becomes swollen, red, and extremely tender to touch.Abdominal Pain
Testicular torsion can cause pain or cramping in the lower abdomen, especially in younger patients.High-Riding Testicle
The affected testicle may be positioned higher than usual in the scrotum, which can make physical examination more challenging.Testicular Discoloration
Reduced blood flow to the testicle may lead to darkening or discoloration of the skin around the affected area.Testicular Torsion in Children
Children may present additional symptoms, such as abdominal discomfort, vomiting, irritability, and noticeable swelling or redness in the scrotum.
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. Rapid diagnosis and treatment, usually through surgical intervention, are critical to saving the testicle and preventing complications.
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Diagnostic Tests Before Testicular Torsion Surgery
When testicular torsion is suspected, doctors often perform a physical examination along with diagnostic tests to confirm the condition and rule out other potential causes of symptoms. Here are the common tests conducted before surgery:
Ultrasound
An ultrasound with Doppler imaging helps assess blood flow to the testicle. Reduced or absent blood flow is a strong indication of testicular torsion.Blood Tests
Blood tests may be used to detect signs of infection or inflammation in the body, which can sometimes mimic the symptoms of torsion.Urine Tests
A urine test is commonly conducted to exclude urinary tract infections (UTIs) or other conditions that might cause scrotal pain or discomfort.
Prompt diagnosis and testicular torsion treatment are critical, as delays in intervention can lead to permanent damage or loss of the affected testicle.
Testicular Torsion Surgery
Surgery is the most effective treatment for testicular torsion, and it is usually required immediately after diagnosis. The primary goal is to restore blood flow to the twisted testicle. Treatment options include:
Medication
Pain relief medications may be prescribed to manage the intense discomfort associated with torsion.Manual Detorsion
In some cases, the doctor may attempt manual detorsion to untwist the testicle and restore blood flow. This procedure is typically performed under anesthesia to minimize pain and discomfort.Surgery (Orchiopexy)
Surgical intervention is the most reliable treatment. During the procedure:- The surgeon untwists the spermatic cord to restore blood flow.
- The affected testicle is secured to the scrotum using sutures to prevent future torsion.
- In severe cases where the testicle is damaged beyond repair due to prolonged lack of blood flow, the testicle may need to be removed (orchiectomy).
Importance of Timely Treatment
Immediate treatment is essential to avoid permanent testicular damage or loss. Delays in restoring blood flow can result in tissue death, infertility, or long-term complications. If you experience sudden and severe testicular pain, seek medical attention without delay.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Benefits of Testicular Torsion Surgery
The benefits of testicular torsion surgery often depend on the timing and severity of the condition. Immediate surgical intervention offers the following advantages:
Salvage of the Testicle
Surgery restores blood flow to the affected testicle, preventing the need for its removal.Fertility Preservation
By saving the testicle, surgery helps maintain fertility and reduces the risk of future infertility.Pain Relief
The surgery alleviates the intense pain caused by torsion, improving the patient’s overall comfort.Prevention of Complications
Early intervention helps avoid serious complications, such as testicular infarction or tissue death due to prolonged blood supply loss.Improved Quality of Life
Treating torsion promptly relieves pain and discomfort, enhancing the patient’s mental and physical well-being.
Causes of Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood flow to the testicle. Common causes include:
Inadequate Fixation
In some individuals, the testicle may not be securely attached to the scrotum, increasing the likelihood of twisting.Physical Activity
Sudden or forceful movements, such as during sports or exercise, can lead to torsion.Trauma
Injury to the scrotum can result in the twisting of the testicle.Congenital Abnormality
Conditions like the “bell clapper” deformity, where the testicle is improperly anchored, raise the risk of torsion.Age
Adolescents and young adults aged 12–18 are most commonly affected.
In some cases, the exact cause remains unknown. Sudden and severe testicular pain warrants immediate medical attention.
Risks and Complications of Testicular Torsion
Delays in treatment can lead to serious complications, including:
Loss of the Testicle
Prolonged blood supply loss can result in the death of the affected testicle.Infertility
Damage to or removal of the testicle may impact fertility, especially if the other testicle is compromised.Chronic Pain
Persistent testicular pain may occur even after surgery.Psychological Impact
Concerns about fertility, sexual function, and body image can cause stress and anxiety.Recurrent Torsion
In some cases, the testicle may twist again after surgery if not properly anchored.Surgical Risks
Surgery carries the potential for infection, bleeding, or accidental injury to nearby structures.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical to minimizing these risks and ensuring the best outcome for the patient.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Precautions After Testicular Torsion Surgery
Proper aftercare is essential to ensure a smooth recovery and prevent complications. Below are the key precautions to take following testicular torsion surgery:
Get Adequate Rest
Rest is crucial in the first few days after surgery. Avoid physical activities and allow your body to heal naturally.Limit Strenuous Activities
Avoid heavy lifting, intense exercise, or activities that place strain on the groin for several weeks as advised by your doctor.Wear Supportive Underwear
Use snug-fitting underwear or a jockstrap to minimize swelling and provide support to the affected area.Follow Pain Management Instructions
Take prescribed pain medications as directed to manage discomfort. Avoid over-the-counter drugs unless approved by your doctor.Monitor for Signs of Infection
Watch for symptoms such as redness, swelling, warmth, pus discharge, or fever. If these occur, contact your healthcare provider immediately.Attend Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-ups allow your doctor to monitor your recovery and address any concerns early.Practice Good Hygiene
Keep the incision site clean and dry. Follow your doctor’s instructions for wound care to prevent infections.Avoid Sexual Activity
Refrain from sexual activity or ejaculation until cleared by your doctor to avoid strain on the surgical site.Stay Hydrated and Eat Well
A healthy diet and sufficient hydration can aid recovery and promote healing.Communicate with Your Doctor
If you experience unusual symptoms like increasing pain, swelling, or difficulty urinating, reach out to your medical team for guidance.
By adhering to these precautions and maintaining open communication with your doctor, you can help ensure a successful recovery from testicular torsion surgery.