Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Varicocele - Treatment Procedure & Benefits at Curific Health Care
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
What is Varicocelectomy Surgery ?
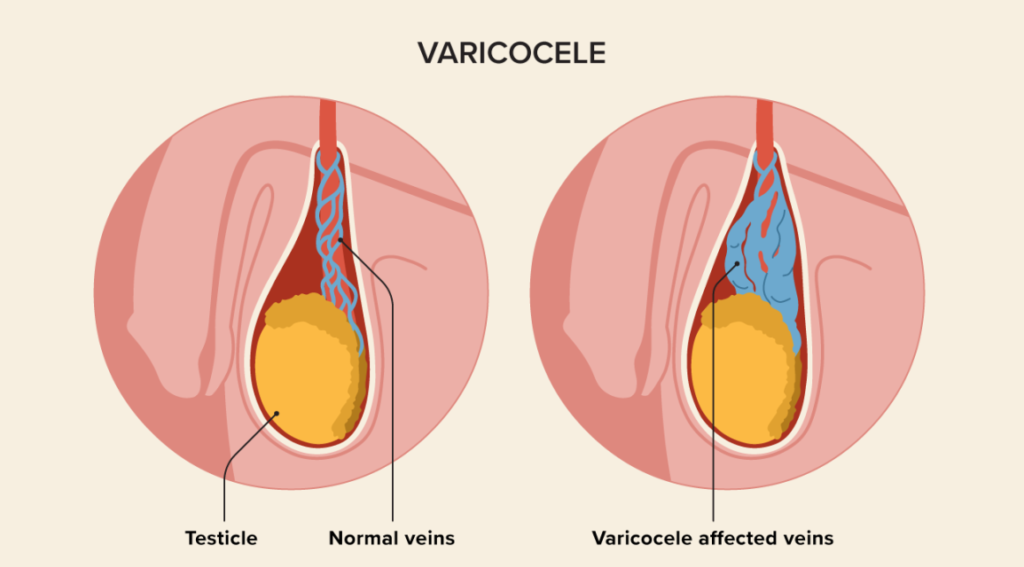
Varicocelectomy is a surgical procedure used to treat varicoceles, which are enlarged veins within the scrotum that can lead to discomfort or fertility issues. The surgery involves removing or tying off the affected veins to restore normal blood flow. By improving circulation and reducing blood pooling, varicocelectomy can relieve symptoms like pain, heaviness, or testicular shrinkage. In cases where fertility is affected, the procedure can help improve sperm production by reducing the excess heat caused by the varicocele.
The surgery is typically performed under local or general anesthesia and can be done using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic or microsurgical varicocelectomy. The choice of technique depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s specific needs.
Varicocelectomy is generally considered safe, with a high success rate in reducing symptoms and improving fertility outcomes for many men. However, as with any surgery, there are potential risks, including infection, bleeding, and recurrence of the varicocele. Recovery time is typically short, and most men can return to normal activities within a few days, though strenuous activities may be restricted for several weeks.
In the early stages, varicose veins may present as spider veins or leg pain, though the condition may also remain asymptomatic for long periods. Venous insufficiency is a common cause, which develops gradually in stages. The stages of varicose veins are:
Stage 1: Spider Veins
These are dilated capillaries that form a web-like pattern on the affected area. They occur when the capillaries are compressed due to an underlying issue.
Stage 2: Varicose Veins
These rope-like veins bulge outward due to blood pooling in them. They are clearly visible as they affect superficial veins.
Stage 3: Leg Edema
Excessive blood pooling causes chronic swelling or edema in the legs, often accompanied by restless leg syndrome and severe cramping.
Stage 4: Skin Changes
As the condition progresses, skin discoloration may appear along with thin, brown spots from blood leaking into the skin tissues.
Stage 5: Leg Ulcers
If left untreated, painful and itchy skin ulcers may form, requiring ongoing care and monitoring.
Many people ignore varicose veins, thinking the condition is not serious or will resolve on its own. However, untreated varicose veins can lead to life-threatening complications. Seeking help from a vascular specialist is crucial for proper treatment.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Varicocele Diagnosis
The diagnosis of varicocele typically involves a combination of a medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes additional diagnostic tests. Here is an overview of the diagnostic process to identify the severity and determine the best approach for varicocele surgery:
Medical History: The doctor will begin by discussing the symptoms and medical history before attempting surgery for varicocele. They may ask about any pain, discomfort, or fertility concerns that are exhibited by the patient.
Physical Examination: A physical examination is a crucial step in diagnosing varicocele. The doctor will perform a thorough examination, including inspecting and palpating the scrotum while you are standing. They will look for enlarged or twisted veins and assess the size and consistency of the testicles. Typically, varicoceles can be felt as a mass of dilated veins above the testicle, often described as feeling like a “bag of worms.”
Valsalva Maneuver: The Valsalva Maneuver is a breathing technique where the doctor asks the patient to stand and breathe out through the mouth while holding the nose shut. The patient is asked to take deep breaths while the doctor holds the testicle in their palm and feels the scrotum. This maneuver helps to find enlarged veins in the scrotum.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend additional tests to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the varicocele.
Scrotal Ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create a detailed image of the scrotum and its structures. It can help visualize the dilated veins, assess blood flow, and rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
Doppler Ultrasound: This is a specialized type of ultrasound that evaluates blood flow before the surgery for varicocele. It can provide information about the direction and speed of blood flow in the veins, helping to determine the severity of the varicocele.
Semen Analysis (if fertility concerns exist): If the patient is experiencing fertility issues, the doctor may recommend a semen analysis. This test assesses various parameters of sperm health, such as sperm count, motility, and morphology. While varicoceles can potentially affect fertility, not all men with varicoceles experience infertility.
Based on the findings from the medical history, physical examination, and any additional tests, your doctor will be able to confirm the diagnosis.
Get In Touch
Make an Appointment
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Varicocele Surgery Options
Treatment options for varicocele can be categorized into surgical and non-surgical approaches. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of symptoms, impact on fertility, and personal preferences.
The surgical treatment for varicocele is called Varicocelectomy Surgery. It can be performed through different techniques, including open surgery (inguinal or subinguinal approach) or minimally invasive laparoscopic or microscopic procedures. The procedure involves accessing the affected veins, tying them, and/or removing them. This redirects the blood flow to the healthier veins and provides relief from the symptoms.
- Open varicocele surgery is invasive as it involves making large incisions in the groin or scrotum to access the vein.
- However, with laparoscopic and microscopic techniques, varicocele surgery is made minimally invasive, allowing faster recovery and lower recurrence rates.
- Laser surgery for varicocele helps seal the affected spermatic veins with the help of the diode laser. This method promotes a quick and smoother recovery.
The non-surgical treatment option is Varicocele Embolization, also known as percutaneous embolization. This minimally invasive procedure is performed by an interventional radiologist and involves the insertion of a small catheter through a vein. Coils or sclerosing agents are then used to block the affected veins. Embolization is an alternative to surgery, particularly for individuals who may not be suitable candidates for surgery or prefer a non-surgical approach.
If the varicocele is not causing significant symptoms or fertility issues, a conservative approach focusing on managing discomfort or pain may be recommended. This can include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen)
- Scrotal support garments (e.g., athletic supporters or compression underwear)
- Lifestyle modifications (e.g., avoiding prolonged standing or strenuous activities)
It is important to note that not all varicoceles require treatment. If the varicocele is asymptomatic, not affecting fertility, and causing no significant discomfort, observation without intervention may be an appropriate approach. Regular monitoring and follow-ups with the doctor are essential to assess any changes in symptoms or fertility status.
Varicocele Surgery (Varicocelectomy Surgery)
The purpose of varicocele surgery is to seal the enlarged and malfunctioning vein in the scrotum and redirect it to the healthy veins. This is best performed with laser surgery for varicocele. Once this is done, the testicle returns to its normal size, and other issues are also addressed.
The surgery requires general anesthesia and is usually performed on an outpatient basis. Depending on the technique being used, the procedure may take around 1 to 2 hours or more in complex cases. The most suitable technique—whether open varicocele surgery, microscopic surgery, or laparoscopic surgery—is chosen depending on the severity of the condition.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Benefits of Surgical Treatment for Varicocele
Surgical treatment for varicocele (Varicocelectomy Surgery) offers several potential benefits. Here are the primary advantages of varicocele surgery:
- Relief from Symptoms: Varicocele surgery helps reduce the pressure caused by the dilated veins, relieving symptoms such as aching, heaviness, or dragging sensations in the scrotum.
- Improvement in Fertility: Many patients experience improved testicular function and sperm production after varicocele surgery. This leads to better sperm count, motility, and morphology, potentially increasing the chances of natural conception.
- Preventative Measures: In men who don’t have fertility issues, varicocele surgery may be recommended as a preventative measure to avoid future problems with conception.
- Low Risk of Recurrence: Varicocelectomy Surgery, especially microscopic varicocelectomy, has a minimal risk of recurrence. The surgery preserves key structures while addressing the issue effectively.
In addition to these advantages, the advanced minimally invasive techniques used for varicocele surgery, such as laparoscopic and microscopic varicocelectomy, offer further benefits to patients:
- Smaller Incisions: Minimally invasive surgery is performed through tiny incisions using a laparoscope or microscope and other small surgical instruments.
- Less Pain: The surgery causes minimal pain during and after the procedure, requiring fewer medications and allowing the patient to resume regular activities quickly.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients undergoing minimally invasive surgery typically don’t need to stay in the hospital for more than 24 hours, as their vitals return to normal quickly.
- Quicker Recovery: Due to the smaller incision size, the wound heals quickly and smoothly, leading to a faster recovery compared to open surgery.
- Less Scarring: As the incisions are tiny, they heal without leaving visible scars. Stitches, if used, often disappear over time without leaving permanent marks.
- Increased Accuracy: The minimally invasive techniques use tools like a laparoscope and microscope, which provide clear visualization of internal organs. This allows the procedure to be carried out with high precision, improving the success rate of the surgery.
Preparation Before Varicocele Surgery
Before varicocele surgery, the doctor will provide detailed instructions to ensure the patient is well-prepared for the procedure. These general instructions typically include the following:
- Pre-surgery Tests: The doctor may recommend some tests to assess the severity of the condition and determine the safest treatment approach.
- Medication Review: The patient should inform the doctor about all prescribed and over-the-counter medications and supplements being taken. The doctor may adjust these medications and recommend discontinuing certain supplements temporarily.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: It is important to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol before surgery to improve overall health and reduce potential risks during the procedure.
- Blood-thinning Medications: The patient may be advised to stop taking aspirin or other blood-thinning medications, as these can increase the risk of excessive bleeding during the surgery.
- Fasting: The patient should refrain from eating or drinking for 6-8 hours before the surgery, as food or liquid in the stomach may interfere with anesthesia and pose a risk of aspiration.
- Hygiene: On the day of surgery, the patient should take a shower with antibacterial soap and wear clean, comfortable clothing.
- Health Issues: If the patient is feeling unwell, has a cold, or experiences any other health issues, they should inform the doctor as the surgery may need to be rescheduled.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Before and After Varicocele Surgery
Varicocele is a condition where the veins in the scrotum become enlarged, leading to symptoms such as pain, discomfort, or a heavy feeling. It can also impact fertility by affecting the temperature regulation of the testicles and interfering with sperm production. The surgical procedure, known as varicocelectomy, aims to repair the affected veins and alleviate these issues. Below is an overview of what to expect before and after varicocele surgery:
Before Surgery:
- Symptoms: Varicoceles can cause scrotal pain, discomfort, or a heavy feeling, and may also be linked to fertility problems due to their impact on sperm production.
- Grade III Varicocele: In more severe cases, where varicoceles are visible, laser surgery can not only address symptoms but also improve the cosmetic appearance of the scrotum.
- Fertility Concerns: Varicoceles can affect sperm quality and count, so surgery may be recommended to enhance fertility.
After Surgery:
- Improvement in Symptoms: The surgery is aimed at reducing pain, discomfort, and improving fertility by repairing the veins and restoring normal blood flow.
- Reduction in Swelling and Bruising: After surgery, there is typically less swelling and bruising in the scrotal area, and these improve over time as recovery progresses.
- Resumption of Sexual Activity: Most patients can resume sexual activities without pain or discomfort once they have fully recovered from the surgery.
Recovery After Varicocele Surgery
Recovery after varicocele surgery depends on the type of surgery performed. Here is a general guideline based on the surgical approach:
Open Varicocelectomy (inguinal or subinguinal approach):
- Hospital Stay: This surgery is typically done on an outpatient basis, meaning no overnight stay is required.
- Recovery Time: Most individuals can resume normal activities within 1 to 2 weeks. However, complete recovery may take up to 4 weeks.
- Return to Work/School: Depending on the nature of the work or school activities, patients may need to take 1 to 2 weeks off.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting for 2 to 4 weeks post-surgery to prevent complications.
Laser Surgery for Varicocele:
- Recovery: Laser surgery is minimally invasive and generally offers a faster recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. Most patients experience smoother and quicker healing, with less pain and bruising.
Following post-surgery instructions carefully, including avoiding heavy activities and attending follow-up appointments, is crucial to ensure a successful recovery.
Microsurgical Varicocelectomy & Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy Surgery
Hospital Stay:
- Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: This is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, meaning the patient can go home on the same day.
- Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy: This procedure may require an overnight hospital stay due to its more invasive nature compared to microsurgical surgery.
Recovery Time:
- Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: Recovery time is generally faster than open surgery, with most individuals able to resume normal activities within a few days to a week.
- Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy: Recovery is also quicker than open surgery, but may take slightly longer than microsurgical surgery.
Return to Work/School:
- Patients typically need to take a few days to a week off before returning to work or school, depending on the nature of their activities.
Exercise and Physical Activity:
- Strenuous exercise and heavy lifting should be avoided for about 2 weeks after surgery to ensure proper healing and prevent complications.
Risks & Complications Associated with Varicocele Surgery
Although varicocele surgery is generally safe, like all surgical procedures, it carries some risks and potential complications. Here are some to be aware of:
Infection:
- Risk: While rare, infections at the surgical site can occur. Proper hygiene, sterile techniques, and appropriate post-surgery care help minimize this risk.
Excessive Bleeding:
- Risk: Bleeding during or after surgery is possible, though it is usually controlled during the procedure. In rare cases, further treatment may be required.
Hematoma:
- Risk: Blood accumulation can form a hematoma, which may resolve on its own or require drainage in some cases.
Damage to Surrounding Structures:
- Risk: Although uncommon, unintentional damage to nearby structures, such as blood vessels, nerves, or the vas deferens, may occur. Experienced surgeons minimize this risk.
Recurrence:
- Risk: There is a small chance of recurrence, though microsurgical varicocelectomy generally has a lower recurrence rate compared to other methods.
Pain or Discomfort:
- Risk: Some patients may experience residual pain due to factors like nerve irritation or remaining varicose veins. However, significant persistent pain is rare.
Anesthetic Risks:
- Risk: If general anesthesia is required, there are minimal risks involved, including allergic reactions or respiratory issues. These risks are usually managed by an experienced anesthesiologist.
Patients should discuss these potential risks with their surgeon, who will provide guidance on how to minimize them and ensure the best possible outcome from the surgery.
Make An Appointment
Simplifying Surgery Experience
Consult with our expert surgeon for more than 50+ diseases
- Once you share your details, our care coordinator will get in touch with you.
- The coordinator will understand your symptoms and health condition in detail.
- Your consultation will be scheduled at the earliest.
Lifestyle Changes After Varicocele Surgery
Adopting healthy lifestyle changes after varicocele surgery is essential for a smooth recovery and to promote overall well-being. Here are some general tips to follow:
Rest and Recovery
- Rest is crucial for the healing process. Follow the surgeon’s instructions regarding rest and avoid strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting or intense exercise, during the specified recovery period. Gradually resume activity as advised.
Scrotal Support
- Scrotal support garments, such as athletic supporters or compression underwear, provide comfort and help reduce swelling during recovery. They also promote circulation and alleviate discomfort.
Pain Management
- Take the prescribed medications as directed to manage pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like acetaminophen, are typically sufficient. If pain persists, consult the doctor for an adjusted prescription or stronger pain medication.
Healthy Diet
- A balanced diet is key for recovery. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Adequate hydration is also important for the healing process.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
- Refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol during the recovery period. Smoking can slow down healing, while alcohol can interfere with medications and cause dehydration.
Gentle Exercise
- Light physical activity, such as walking, can improve blood circulation and help prevent blood clots. However, avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting for the first few weeks after surgery.
Follow-up Appointments
- Attend follow-up appointments to monitor recovery. These visits allow the doctor to evaluate the healing process, address concerns, adjust medications, and offer further guidance.
Abstain from Sexual Activities
- While sexual function typically returns to normal after surgery, it is advised to abstain from sexual activities for 2 to 3 weeks. This helps prevent internal bleeding and reduces strain on stitches. The doctor will approve when it’s safe to resume sexual activity.
By following these recovery tips, you can ensure a successful healing process and return to normal activities as soon as possible.
Non-Surgical Treatment of Varicocele
While surgery is the most common treatment for varicocele, varicocele embolization offers a non-surgical alternative. This minimally invasive procedure, performed by an interventional radiologist, involves blocking the affected veins using a catheter.
The Process of Varicocele Embolization:
- The interventional radiologist makes a small incision, typically in the groin or neck area.
- A catheter is inserted into a vein and guided to the site of the varicocele using X-ray guidance.
- Small coils or embolic agents (such as tiny particles or foam) are placed into the affected veins to block them.
- Once the blood flow is redirected, the varicocele shrinks, and symptoms improve.
Advantages of Varicocele Embolization:
- Minimally invasive: Performed through a small incision, leading to minimal scarring and tissue trauma.
- Outpatient procedure: Can often be performed on an outpatient basis, leading to quicker recovery.
- Less anesthesia risk: Usually done under local anesthesia or mild sedation, avoiding the risks of general anesthesia.
- Short recovery time: Most individuals can resume normal activities within a few days.
However, varicocele embolization may not be suitable for all cases.
Home Remedies for Varicocele Symptoms
While home remedies cannot cure varicoceles, they can help manage symptoms and provide relief. These can be used alongside medical treatment or as a means to alleviate discomfort.
- Scrotal Support: Wear supportive underwear or a jockstrap to alleviate discomfort and prevent sagging of the scrotum.
- Cold Compress: Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and pain. Wrap ice in a cloth and apply it for 10-15 minutes at a time, multiple times a day.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling to improve circulation and promote testicular health.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated, avoid excessive alcohol, and quit smoking to support overall vascular health.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting/Standing: Change positions regularly and avoid sitting or standing for long periods to reduce pressure on the affected veins.
These remedies provide temporary relief but do not address the underlying cause. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper treatment.
How to Prevent Varicocele
Although varicocele can’t always be prevented, adopting certain lifestyle and dietary changes can reduce the risk:
- Maintain vascular health: Keep your blood pressure and body weight in check.
- Active lifestyle: Avoid sedentary habits and engage in regular physical activity.
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of fluids to maintain proper circulation.
- Avoid excessive pressure: Minimize activities that stress the groin area.
- No smoking: Smoking can contribute to vascular issues and increase the risk of varicocele.
Testicle Size After Varicocele Surgery
After varicocele surgery, testicular size may vary depending on the severity of the varicocele, the success of the surgery, and the individual’s healing process. If the varicocele caused testicular atrophy (shrinkage), the testicle may return to its normal size after surgery. However, full restoration to its original size is not guaranteed. It’s important to follow up with your healthcare provider to monitor recovery and address any concerns regarding testicular size or other post-surgery issues.